If you are preparing for CLAT or other law entrance exams, you have probably heard seniors, teachers, or toppers repeatedly say this
“Legal reasoning is different from logical reasoning.”
At first, this statement sounds confusing. Both sections involve thinking, reasoning, and choosing the most logical answer. So why are they treated as two separate sections? More importantly, how should you prepare for each one differently?
This article is written to clear that confusion once and for all. By the end of this guide, you will clearly understand what logical reasoning is, what legal reasoning is, how they are different, and how you should approach both sections strategically for CLAT.
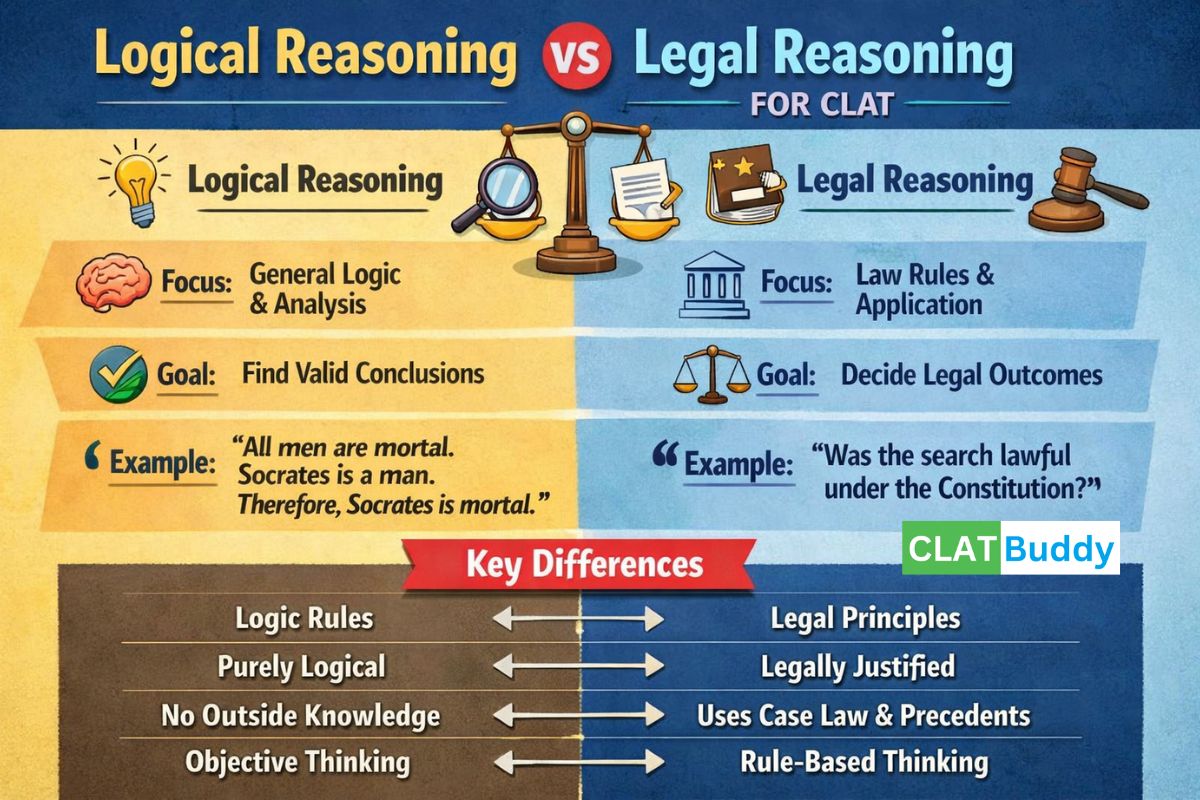
Logical reasoning is a section that tests your ability to think clearly, analyse information, and draw correct conclusions based on given facts. It is not about law at all. It is about how your brain processes information.
In CLAT, logical reasoning questions usually come in the form of passages. These passages talk about social issues, arguments, opinions, or situations. Your job is to read carefully and answer questions based only on the information given in the passage.
Logical reasoning checks whether you can
You are not expected to bring outside knowledge. Everything you need is inside the passage.
Logical reasoning is important because law as a career demands structured thinking. Lawyers, judges, and legal professionals constantly analyse arguments and identify flaws in reasoning.
For CLAT, this section tests whether you can
If you master logical reasoning, you automatically improve your performance in reading comprehension and even legal reasoning.
Legal reasoning is where CLAT starts testing your legal aptitude. This section introduces you to how law actually works, even before you enter law school.
In legal reasoning, you are given
Your task is to assume that the legal principle given is correct and apply it logically to the situation, even if you personally disagree with it.
Legal reasoning does not test your knowledge of law. It tests your ability to apply a rule objectively.
CLAT is an entrance exam for law schools. Naturally, it wants to check whether you have the basic mindset required for studying law.
Legal reasoning tests whether you can
If logical reasoning trains your brain, legal reasoning trains your legal mind.
Many students think legal reasoning is just logical reasoning with legal words. This is not true. The difference lies in the approach, not the difficulty.
Logical reasoning focuses on general thinking skills. Legal reasoning focuses on rule application.
In logical reasoning, you decide whether an argument makes sense.
In legal reasoning, you decide what the law says should happen.
In logical reasoning, your answer depends on logic alone.
In legal reasoning, your answer depends on how the legal rule applies, not on what feels right.
Understanding this difference is crucial because using the wrong approach can cost you marks.
Logical reasoning tests analytical thinking. You are expected to engage with the passage, break down arguments, and evaluate reasoning patterns.
Common Skills Tested in Logical Reasoning
In this section, personal opinions do not matter. Only what logically follows from the passage matters.
Logical reasoning rewards students who read slowly, think deeply, and avoid jumping to conclusions.
Legal reasoning tests rule based thinking. You are expected to follow a structure similar to what lawyers use.
The structure usually looks like this
This method is often called the principle application approach.
Understanding legal principles
Legal reasoning rewards students who respect the rule given and apply it mechanically, even if the result feels harsh.
This is where many students make mistakes.
In logical reasoning, you are asked to identify hidden assumptions. You question the argument and check what is being taken for granted.
In legal reasoning, you do not question the principle. You accept it fully and apply it as it is.
If you start questioning the fairness of a legal rule in legal reasoning, you will likely choose the wrong answer.
One of the biggest traps in legal reasoning is morality.
Many legal principles in CLAT are intentionally designed to clash with your sense of right and wrong. This is done to check whether you can separate law from personal beliefs.
In logical reasoning, moral thinking might sometimes help if it aligns with the argument.
In legal reasoning, moral thinking almost always harms your answer.
You must constantly remind yourself. This is not about what should happen. This is about what the rule says should happen.
Preparing logical reasoning is about building thinking habits.
The goal is not just solving questions but improving how you think.
Preparing legal reasoning is about learning to apply rules consistently.
Practical Tips for Legal Reasoning Preparation
Read the legal principle multiple times
Legal reasoning becomes easier when you stop overthinking and start following the structure.
Both sections are scoring if prepared correctly, but for different reasons.
Logical reasoning is scoring if you have strong reading and analytical skills. Legal reasoning is scoring if you have discipline and rule based thinking.
Students who rely too much on intuition struggle in legal reasoning. Students who rush through passages struggle in logical reasoning.
The smartest strategy is to treat both sections differently and respect their unique demands.
Understanding mistakes is as important as understanding concepts.
Avoiding these mistakes alone can significantly boost your score.
CLAT is not just an entrance exam. It is a filter.
Logical reasoning prepares you for
Legal reasoning prepares you for
If you master both now, your transition into law school becomes much smoother.
If there is one takeaway from this article, it is this
Logical reasoning and legal reasoning are not rivals. They are complementary skills.
Logical reasoning teaches you how to think.
Legal reasoning teaches you how to think like a lawyer.
Treat them differently. Prepare them differently. Practice them differently.
If you do this consistently, not only will your CLAT score improve, but your confidence as a future law student will grow as well.